Since uncertified materials, such as polyvinyl chloride (PVC), can emit hazardous compounds, using the proper food-grade plastics is essential for safe storage.
Bioplastics, such as PHA and PETE, are gaining traction as sustainable alternatives that offer food safety, compostability, and a reduced carbon footprint. Selecting the right materials for food storage necessitates a thorough understanding of food-safe plastics and their components.
What Does Food-Safe Plastic Mean?
Food-grade plastics are materials tested to prevent harmful substances from leaching into food and causing damage. They meet strict standards and guidelines set by the U.S. FDA and European EFSA, ensuring chemical safety, durability, and resistance to toxins.
Studies show that food-grade plastic, free from harmful additives and compounds, is vital for ensuring the safety of food products in the food industry.
Compliance with these regulations is essential for consumer health, food processing, and maintaining the integrity of food products, aligning with the industry’s values of sustainability and safety.
What are the Safest Plastics to Use in Food Containers?
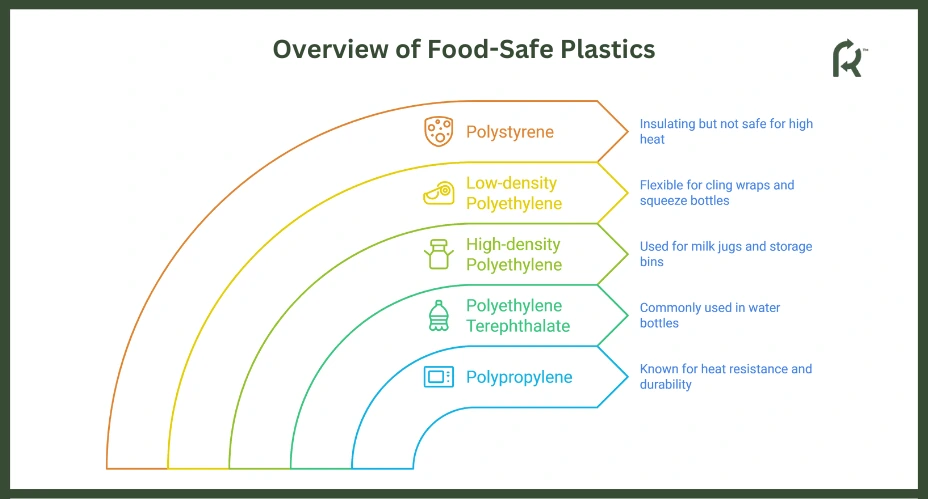
Polypropylene (PP) is ideal for microwave-safe food storage containers due to its strength and heat resistance. Polyethylene Terephthalate (PET) is straightforward and commonly used in water bottles.
High-density polyethylene (HDPE) is robustly used for items like milk jugs and storage bins, while low-density polyethylene (LDPE) is flexible for cling wraps and squeeze bottles. Bioplastics like PLA and PHA, made from renewable resources, offer food safety and compostability. These plastics are tested to prevent chemical leaching, ensuring consumer safety.
PHA: The Most Sustainable Option Amongst Food-Safe Plastics
PHA is a cutting-edge material made from renewable resources, offering unmatched benefits for food storage while aligning with both safety and sustainability goals.
Key Features of PHA for Food Storage:
- 100% Biodegradable and Compostable: PHA naturally breaks down into non-toxic components, leaving no harmful residues behind, even in marine environments.
- FDA-Approved for Food Contact: Compliant with strict food safety regulations, making it safe for a wide variety of food packaging applications.
- Durable and Versatile: While being eco-friendly, PHA is also highly durable and resistant to moisture, grease, and oils, ensuring long-lasting performance for food storage.
- Free of Harmful Additives: PHA does not rely on petroleum-based chemicals or harmful plasticizers, ensuring safety for human health.
- Circular Economy Integration: PHA production utilizes agricultural byproducts or waste, reducing reliance on virgin materials and contributing to a circular economy.
Polyethylene (PE)
Both high-density (HDPE) and low-density (LDPE) polyethylene (PE) are food-safe because of their durability, non-reactivity, and resistance to chemicals.
While LDPE’s elasticity makes it perfect for food packaging, HDPE is a good choice for rigid containers.
It is ideal for applications involving food contact because it is resistant to moisture at various temperatures, which reduces the possibility of contamination.
Polypropylene (PP)
Polypropylene (PP) is a versatile, food-safe plastic known for its heat, moisture, and chemical resistance. It is lightweight, durable, and commonly used in yogurt cups, takeaway containers, and straws.
PP doesn’t leach harmful chemicals into food, making it reliable for long-term storage and high-temperature use.
Polyethylene Terephthalate (PET)
Polyethylene terephthalate (PET) is commonly used in food and beverage packaging for its safety, lightweight nature, and excellent barrier properties.
PET keeps products fresh by preventing moisture and gas transfer in water bottles, soda bottles, and food trays. PET is FDA-approved for food contact, and its recyclability makes it a practical and eco-friendly packaging choice.
Polystyrene (PS)
Due to its low cost and insulating properties, polystyrene (PS) is a good choice for food containers.
However, when heat is exposed, PS can warp or melt, releasing harmful chemicals. Thus, it is not safe for microwave use or high-temperature storage. While convenient for single-use applications, PS is less durable and environmentally friendly than other food-safe plastics.
Polycarbonate (PC)
Polycarbonate (PC) is a durable plastic used in bottles and food containers for its impact resistance and clarity. However, its use has decreased due to concerns over bisphenol A (BPA), a chemical linked to health risks, especially when exposed to heat or acidic foods. Many manufacturers now offer BPA-free alternatives, but consumers should check labels to ensure safety.
Silicone
Silicone is a popular food-safe alternative to plastics due to its durability, reusability, and resistance to chemical leaching, even at extreme temperatures. It is friendly for freezer, microwave, oven, and dishwasher use and is found in reusable food bags and containers. Its longevity and eco-friendly qualities make it an excellent choice for reducing single-use plastic waste.
How to Identify Food-Safe Plastics
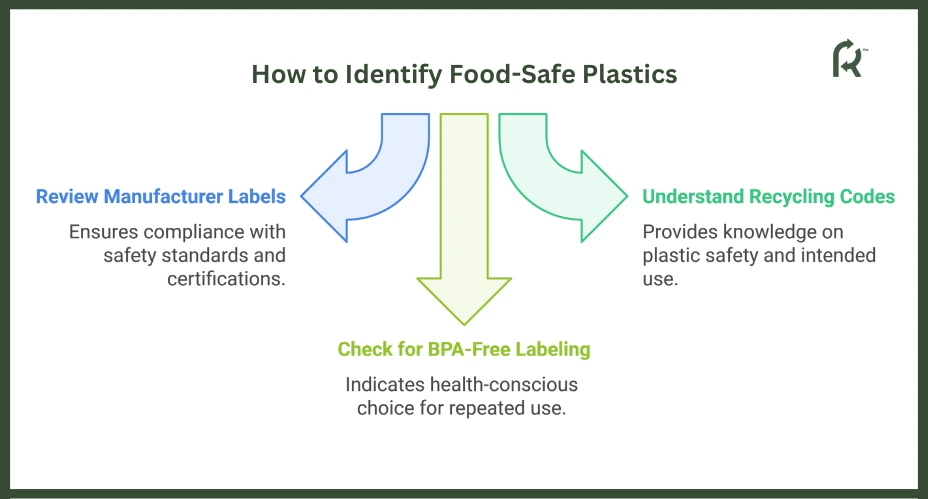
To make informed judgments, businesses and consumers can review manufacturer labels, resin codes, and symbols that indicate suitability for food contact. Plastics that follow strict health and safety standards are assured to be safe, giving you the information you need to make the best decisions for the environment and your health.
Symbols and Codes
Understanding recycling codes is not just about deciphering random numbers; it’s about gaining essential knowledge on plastic safety and intended use. For instance, Code 1 (PET) signifies single-use bottles, while Code 2 (HDPE) indicates durable containers. This understanding allows you to make knowledgeable decisions regarding recycling and food safety, fostering a sense of responsibility and proactivity in managing your plastic use.
Recognizing and comprehending these codes empowers customers to make knowledgeable decisions regarding recycling and food safety, fostering a sense of responsibility and proactivity in managing their plastic use.
Manufacturer Labels
‘Food-safe’ certifications and labeling ensure that products are made from materials that are safe to be touched by food and drink. According to these labels, the product complies with regulations to prevent contamination, leaching, or dangerous chemical reactions.
Certifications from agencies like the FDA or EU are not just stamps on a product; they are reassurances of safety. They signify that the product has passed stringent safety testing, improving food safety and public health. This knowledge should instill confidence in your choices, knowing your product is safe for food contact.
Testing for Safety
It is crucial to look for BPA-free labeling to ensure the safety of plastics for repeated use; BPA can leach into food and pose health risks, so this caution is a sign of your health-conscious approach.
When choosing food-safe plastics, consider the product’s intended use. Some plastics are designed for single use, while others are meant for reuse. Look for certified products, such as those with FDA certifications granted after rigorous safety testing.
Lastly, always check for wear and tear, as broken materials may release dangerous substances. This mindful approach to plastic use signifies your commitment to safety and responsibility.
Potential Risks of Non-Food Safe Plastics
Non-food-safe plastics pose health risks as chemicals like phthalates and BPA can leach into food, especially when exposed to heat or wear. BPA causes endocrine disruption, reproductive issues, and increased risks of heart disease and diabetes.
In contrast, safer plastics like PET and PP are less likely to leach harmful chemicals. PET is commonly used in food containers, which makes it a good choice. With a 30% recycling rate, PET is familiar in food containers, while PP is more durable and safer for repeated use.
Food-Safe Plastic vs. Sustainable Alternatives
Unlike sustainable substitutes for food-safe plastics, biodegradable polymers, glass, and stainless steel have notable environmental advantages. These materials offer safer, more environmentally friendly food packaging and storage options while lowering the amount of plastic trash generated.
1. PHA
PHA (Polyhydroxyalkanoates) is a food-safe, biodegradable, and compostable plastic alternative. Unlike traditional plastics, PHA decomposes naturally, making it eco-friendly for food packaging.
Biocompatible and safe for food contact, REGEN™ PHA offers faster degradation and higher durability than other bioplastics. It meets strict food safety standards, providing a reliable, sustainable option for reducing plastic waste without compromising performance.
2. Glass
Glass is a sustainable, reusable option for food storage, offering both environmental and safety benefits. Non-toxic, resistant to leaching, and fully recyclable, glass reduces the need for new materials. Its reusability minimizes waste, making it an ideal long-term storage solution and an eco-friendly choice that reduces reliance on single-use plastics.
3. Stainless Steel
Stainless steel is a durable option for food storage because it is highly resistant to wear and tear.
Its nontoxicity and reusability reduce waste and prevent dangerous chemicals from leaking into food. Stainless steel is an excellent alternative to traditional plastics because it can be recycled endlessly without losing quality.
4. Biodegradable and Compostable Plastics
Biodegradable and compostable polymers provide food-safe alternatives to conventional plastics that promote environmental sustainability.
These substances decompose organically, lowering pollution over time. In contrast to traditional plastics, which last for centuries, biodegradable polymers break down into non-toxic materials, reducing their adverse effects on the environment.
Compostable plastics improve soil health by returning to the earth as organic materials. In addition to reducing plastic waste, using these environmentally friendly food packaging and storage choices ensures consumer and environmental safety.
Key Takeaways
- Food-safe polymers such as PET, HDPE, and PP provide dependable, long-lasting storage choices.
- By lowering plastic waste and fostering long-term sustainability, sustainable substitutes like glass, stainless steel, and biodegradable plastics offer substantial environmental advantages.
- By selecting these environmentally friendly substitutes, consumers may reduce their influence on the environment while maintaining food safety.
Frequently Asked Questions
Is LDPE Food Safe?
LDPE (Low-Density Polyethylene) is food-safe and widely used for food packaging due to its durability, moisture resistance, and low chemical reactivity. It is commonly found in bread bags, produce bags, and food containers. However, it should not be exposed to high temperatures, as it can soften and potentially leach chemicals.
Do All Food Safe Plastics Need FDA Approval?
Not all food-safe plastics need FDA approval, but the FDA regulates those that come into contact with food to prevent harmful substance leaching. Materials for food packaging, containers, and utensils often require approval. Some plastics bypass individual approval if they adhere to established safety standards or prior evaluations.
Can Food Safe Plastics Be Recycled?
Food-safe plastics like PET and PP can often be recycled. The U.S. recycling rate for PET is about 30%. PP, found in yogurt cups and containers, is recyclable in some areas. Plastics like PVC or those with BPA are not food-safe and pose health risks. Recycling and choosing sustainable alternatives reduce waste and pollution.





