The best option for most biodegradable materials is those designed to naturally decompose through microorganisms, offering a sustainable alternative to traditional plastics that cause significant environmental harm.
Switching to compostable plastics offers numerous environmental benefits, like reduced methane emissions in landfills, replenishment of soil organic matter, and enhanced fertility (EUBP). When choosing the best biodegradable material, their specific characteristics and applications should be considered first.
Certified compostable plastics could be an ideal choice for food packaging purposes and even agricultural films. Meanwhile, PHA is often used for medical implants and farming products. PLA has a meager production cost and is typically used in 3D printing filaments, cups, and straw production.
Lastly, PBAT (Polybutylene Adipate Terephthalate) is an ideal eco-friendly solution where material flexibility is needed, such as in producing plastic bags and mulch films.
What are Biodegradable Materials?
Biodegradable materials can undergo natural hydrolysis by bacterial action into non-toxic components, like water, carbon dioxide, oxygen, and biomass.
A subgroup of these materials, termed compostable materials, undergo complete decomposition in industrial or home composting settings, enriching the soil without polluting it with toxic chemicals.
Unlike petrochemical-based plastics, which have a centuries-long history of atmosphere pollution and the disposal of microplastics, biodegradable materials are a sustainable alternative with a significantly reduced environmental footprint.
For example, BOSK Bioproducts’ REGEN™ PHA products showcase bioplastics’ numerous benefits and potential. REGEN™ materials are produced from renewable resources and are completely compostable while preserving qualities like durability.
In comparison to the widely used PLA, REGEN™ materials offer faster biodegradation. By selecting these biodegradable alternatives, industries and consumers can help combat plastic pollution, which is a pivotal step towards a more sustainable future.
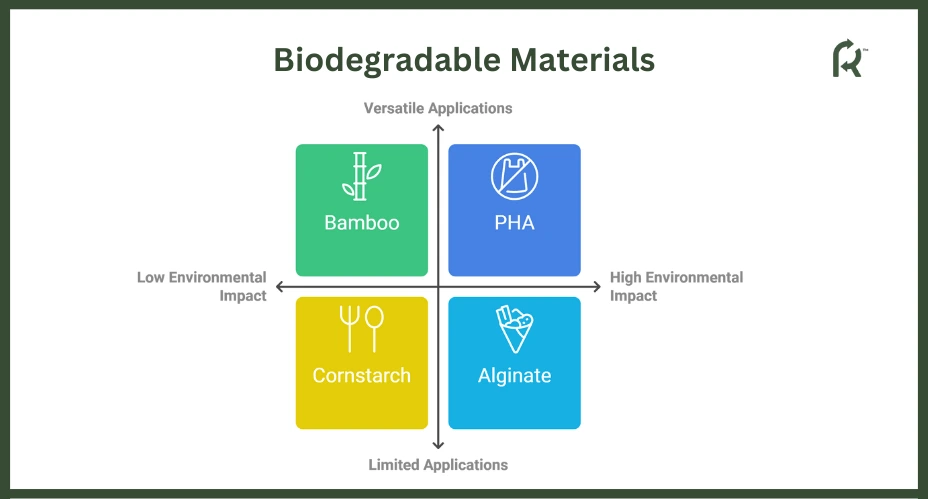
Biodegradable Material Examples
The presence of various biodegradable materials on the market can be overwhelming when choosing a type of biomaterial. However, knowing their differences, specific characteristics, and applications can aid in switching to sustainable alternatives.
1. PHA (Polyhydroxyalkanoate)
Polyhydroxyalkanoates (PHA) are characterized by superior biodegradability and compostability, even in challenging environments, like marine ecosystems, where conventional plastics perform poorly.
Even though PLA requires specific composting conditions, such as temperature and moisture levels, it naturally breaks down in the soil without leaving any toxic residues.
Therefore, PLA is an ideal solution for reducing plastic pollution in the seas and oceans. REGEN™ by BOSK Bioproducts incorporates PHA into its product lineup, providing businesses with an eco-conscious solution while preserving both high-performance and circular economy principles.
2. PLA (Polylactic Acid)
Polylactic Acid (PLA) is a plant-based bioplastic produced from corn, starch, and sugarcane. It is widely used in food packaging, disposable utensils, and 3D printing filaments.
Its affordability and ease of production make it an accessible alternative to fossil fuel-derived plastics. Apart from its practicality, its compostable properties are responsible for its wide use in food and packaging sectors striving to reduce environmental impact.
3. Bamboo
Bamboo has grown in demand. It requires minimal water and no pesticides for growth. It is an excellent choice for producing cutlery, straws, packaging, and fabrics. Bamboo is renowned for its durability, insulation, and environmental benefits, appealing to eco-conscious companies and consumers.
4. Hemp
Hemp is a versatile biodegradable material with a wide range of applications. It offers many benefits since it contributes to the earth’s health and rapid growth cycle.
Hemp fibers produce biodegradable plastics, papers, and textiles, while hemp hurds are used to construct sustainable materials like hempcrete. Its ability to sequester carbon makes it an ideal material for packaging and consumer goods industries.
5. Cornstarch
Cornstarch is a valuable biodegradable material derived from corn. It can be used to manufacture bioplastics like PLA or for disposable cutlery and packaging products. Cornstarch is characterized by fast degradation, reducing landfill waste. Cornstarch products are entirely non-toxic, making them safe for food contact and ideal for food service industries.
6. Wheat Straw
Wheat straw is a biodegradable material produced from the leftover wheat stalks. It reuses agricultural waste, transforming it into various products, like packaging and cutlery. This process of repurposing and its decomposition rate makes it an appealing choice for companies striving for greener solutions.
7. Jute
Jute is a highly sustainable, 100% plant-based material called the “golden fiber.” The crops’ ease of cultivation and ability to enhance soil fertility make it an environmentally friendly crop. This versatile fiber has many application options, from packaging materials and textiles to rugs, clothing, and furniture.
8. Coconut Fiber
Coconut fiber, derived from coconut husk, is used for various applications, such as erosion control mats and gardening soil substitutes. It is characterized by high moisture retention, which makes it suitable for hydroponics and plant growth. Furthermore, it is used in marine applications such as ropes and nets due to its durability and saltwater resistance.
9. Mushrooms
Mushrooms are considered a highly sustainable material due to their mycelium. Mycelium-based packagings combine agricultural waste and mushroom root structure, resulting in lightweight and durable alternatives to traditional plastics.
Alginate
Alginate is a natural polysaccharide that derives from brown seaweed. It is used in biomedical technology to create hydrogels, scaffolds, and delivery systems. Furthermore, it is used for food packaging due to its excellent moisture retention and biodegradability.
What is the Best Option for Biodegradable Materials?
The bioplastics mentioned above all present different sustainability solutions but differ significantly in their breakdown times, environmental impact, and practicality.
PHA stands out with its rapid compostability in industrial settings, while PLA usually requires more extended periods and higher temperatures. Even though they are renewable, bamboo and hemp can take several years to decompose fully.
Cornstarch and wheat straw, on the other hand, break down faster; however, they can contribute to monoculture farming impacts. June and coconut fiber have slower composition rates, while mushroom and alginate materials excel with rapid biodegradation.
Compared to these options, REGEN™ PHA products offer an ideal balance of biodegradability and minimal environmental impact.
Factors to Consider When Choosing Biodegradable Materials
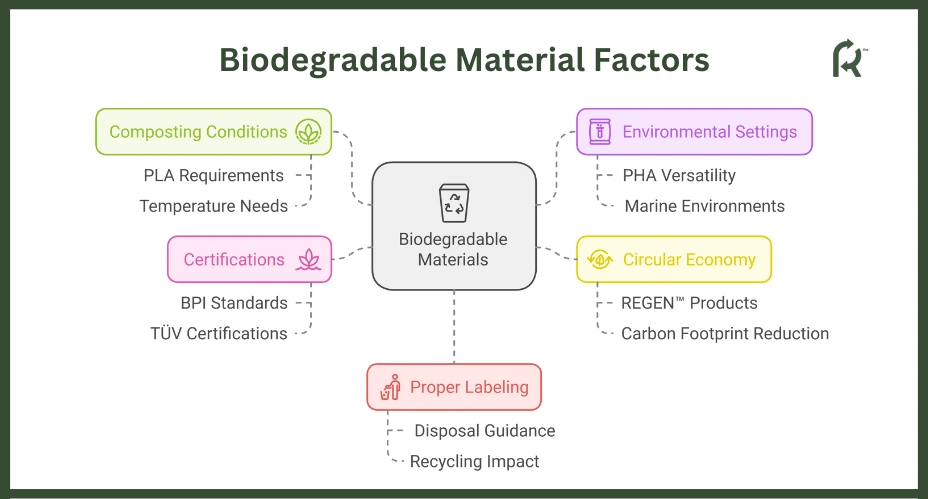
It is important to note that some materials, like PLA, require specific composting conditions, such as high temperatures (around 140°F), and take up to 3-6 months to degrade fully.
Meanwhile, other materials like PHA can biodegrade in different settings, like marine environments and home compost, making it a more sustainable choice. REGEN™ products, by using renewable materials, successfully implement a circular economy and significantly reduce carbon footprint.
Important Considerations
To effectively manage waste, we must understand the differences between compostable and biodegradable materials.
While compostable materials are designed to turn into nutrient-rich compost in controlled settings, biodegradable materials break down; however, they do not fully decompose in landfills.
Certifications like BPI and TÜV can guide consumers in identifying products that align with strict compostability standards. Therefore, proper labeling is essential to ensure the correct disposal of these materials.
Furthermore, accurate labeling can help avoid wasted resources since even biodegradable materials can disrupt traditional recycling if not sorted correctly.
Spotlight on REGEN™ Materials: A Sustainable Solution
REGEN™ materials and products emerge as a sustainable solution characterized by rapid biodegradation and full compostability.
With a faster breaking-down rate than traditional plastics and produced solely from renewable sources, REGEN™ is the perfect choice when pursuing a sustainable practice. Its application is found in various fields, including 3D printing, where it is used for eco-friendly prototypes.
All these qualities enhance product functionality while meeting the increased global demand for eco-friendly alternatives.
Key Takeaways
- REGEN™ dominates in providing sustainable, compostable alternatives to traditional plastics.
- Their biodegradable products break down into harmless components that enrich soil and support ecosystems.
- Through ongoing research and development, Regen sets a standard for eco-friendly practices, proving that high-quality alternatives to single-use plastics can be practical and environmentally sound.
Frequently Asked Questions
1. What is the Most Common Biodegradable Material?
Paper and food waste are among the most common compostable materials. Due to their organic nature, bioplastics like REGEN™ imitate this biodegradability and degrade in less than six months in industrial composting settings.
2. What is the Strongest Biodegradable Material?
REGEN™ PHA is a perfect example of a strong biodegradable material due to its superior performance in various environments and significant flexibility and durability.
3. What Can Consumers Do to Help Promote the Use of Biodegradable Materials?
Consumers can use several strategies to support businesses prioritizing sustainable materials like REGEN™ products. They can raise awareness and educate others about the importance of eco-friendly alternatives.
Furthermore, choosing environmentally conscious products and providing feedback to those businesses is another way to contribute to a greener future. Lastly, staying informed is essential to making more environmentally conscious decisions and promoting sustainability.





