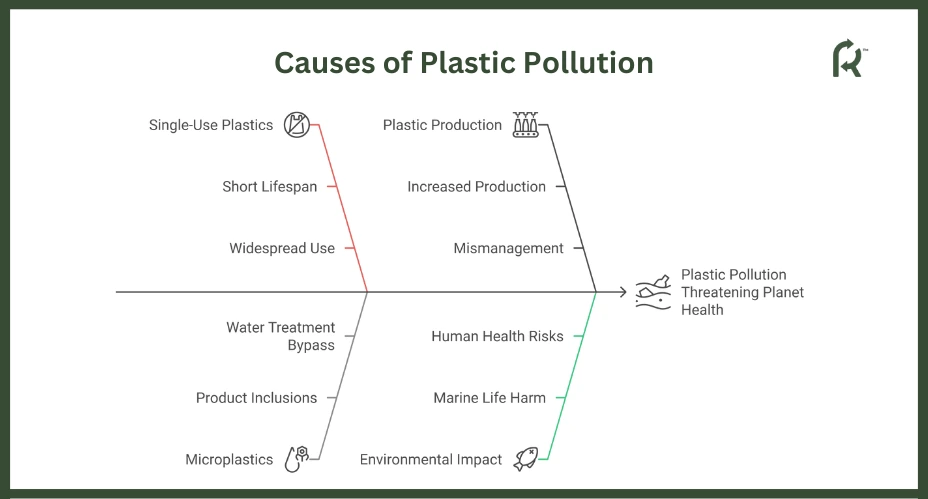
Plastic pollution contributes to biodiversity loss, environmental contamination, and climate change. Production is rising, while waste management remains ineffective.
Addressing plastic pollution involves limiting single-use plastic products and encouraging environmentally friendly alternatives. However, awareness and behavior changes often yield minimal results. We need systemic shifts and significant changes in plastic-related behaviors.
Eco-friendly materials, like BOSK’s bioplastics REGEN™, derived from renewable sources, offer an alternative approach to reducing plastic waste. Bioplastics can biodegrade under specific conditions, such as exposure to certain microorganisms and a controlled composting environment, without releasing toxic by-products.
What is Plastic Pollution?
Plastic production has increased from 1.7 million tons in 1950 to 400 million tons in 2022, with about 25% mismanaged or released into the environment. Single-use plastic bags last only 12 minutes, similar to plastic wraps, cutlery, straws, and coffee cup lids.
Around 20 billion plastic bottles are thrown away each year. Products like facial scrubs, toothpaste, and body wash contain microplastics that slip through water treatment plants, while synthetic fibers from clothing contribute to environmental pollution.
The rising volume of plastic in the environment severely threatens our planet’s health. Transported by wind and currents, plastics enter oceans and accumulate in large current systems called gyres. These toxic substances harm marine life and can enter the human food chain through seafood, leading to serious health issues in humans.
Personal Steps to Reduce Plastic Usage
We heavily rely on single-use plastics (SUPs), which account for 50% of total plastic production. In 2017, 146 million metric tons of plastic were used, mainly for packaging. Cultural norms, convenience, and habits hinder our efforts to reduce SUP usage.
We must create new routines and social norms to shift away from plastic. Changing our behaviors—using reusable items and choosing sustainable products—can help minimize plastic consumption.
Adopting Reusable Alternatives
Here are some simple lifestyle tips to help you reduce your plastic footprint:
- Carry a reusable bottle and silverware to the office and a travel mug to the coffee shop.
- Support a bag tax or ban and carry reusable shopping bags.
- Choose clothing and textiles made of natural materials, like cotton and wool.
- Avoid excessive packaging whenever possible. Instead, choose products in jars and loose fruit and vegetables.
- Approach cosmetics with caution and opt for products with natural exfoliants, like oatmeal or salt.
- Use plastic-free teabags or loose-leaf tea.
- Replace plastic straws with paper or metal ones.
Supporting Plastic-Free Choices
Plastic is integral to modern life, but we can reduce unnecessary waste by changing our behaviors. Developing new habits and routines can help shift our culture away from plastic.
We can make environmentally conscious shopping choices while still enjoying convenient packaging. Alternatives like REGEN™ bioplastics are available, and supporting brands prioritizing sustainable packaging is a great way to minimize plastic waste.

Community Initiatives to Tackle Plastic Waste
The seriousness of the plastic waste problem forces us to reevaluate how we produce, use, and dispose of plastics. Changing our relationship with plastic will take a multi-level and systemic shift.
Community strategies to reduce plastic pollution involve regulatory measures, better waste management, public education, and innovative solutions. A common approach is banning single-use plastics and promoting eco-friendly alternatives, such as installing park drinking stations to encourage tap water consumption.
Transitioning to a circular economy can minimize plastic waste’s environmental impact by focusing on resource recovery and product longevity. Additionally, educational campaigns and voluntary initiatives aim to raise awareness of the harms of single-use plastics, promoting recycling and reusable packaging.
Community Recycling Programs
Community recycling programs, curbside collection, and recycling centers play a significant role in reducing plastic pollution.
The benefits of community recycling programs include:
- Sending less waste to landfills.
- Minimizing community impact on the environment and climate change.
- Reducing greenhouse gas emissions by reducing transportation emissions.
- Improving water and air quality.
- Increasing the number of recyclable materials in the circular economy.
- Fueling the local and regional economy by creating jobs and increasing tax revenue.
- Minimizing costs and saving money on waste management.
- Moving toward sustainable growth in a community.
Awareness of appropriate recycling and waste segregation practices is essential to increasing program effectiveness. Residents can receive educational materials via mail, or drivers on recycling routes can distribute them.
Local Legislation on Plastics
Over 90 countries have enacted laws to reduce the use of plastic bags, particularly lightweight single-use bags. Germany led the way in 1991 by taxing plastic bags, followed by countries like Bangladesh, South Africa, and India in subsequent years.
The United States was slower to act, with San Francisco becoming the first major city to ban single-use plastic bags in 2007. Since then, many states and local governments have implemented similar bans or taxes on plastic products to reduce waste.
In Nepal, an initial ban on single-use plastic bags reduced usage, but weak enforcement allowed retailers to continue distributing them, hindering the uptake of reusable alternatives. This shows that while bans can decrease usage in the short term, effective enforcement and community initiatives are vital for long-term success.
Technological and Industrial Innovations
Technology is vital in addressing plastic waste by enhancing recycling methods, creating new materials, and developing innovative waste management strategies. Around 95% of single-use plastic packaging becomes waste after its first use, with only about 14% collected for recycling and around 4% reused. Additionally, 32% of plastic packaging fails to reach collection centers, ending in waterways worldwide.
Efficient recycling is essential to achieve a functioning plastics circular economy. Recent advancements in artificial intelligence (AI) and near-infrared sensors have significantly enhanced the sorting process, making it easier to differentiate between similar polymer structures.
Advancements in Biodegradable Plastics
Bioplastics are bio-based and biodegradable polymers produced from renewable sources of plant biomass. They are products of microbially fermented and animal-derived polymers that emulate the biomass life cycle by producing water and CO2.
Bioplastics like polyhydroxyalkanoates (PHA) and polylactic Acid (PLA) are emerging as sustainable alternatives to traditional plastics, showcasing eco-friendly innovations.
REGEN™’s PHA is fully compostable and exhibits high strength and heat resistance. REGEN™ provides high-quality PHA filaments optimized for 3D printing.
REGEN™ adopts circular economy principles and encourages sustainable consumption and production patterns. Its production aligns with carbon neutrality goals and replaces single-use plastics with sustainable alternatives, making it an environmentally beneficial choice.
Overall, REGEN™ is committed to combining performance with sustainability in bioplastic innovation.
Recycling Technology Improvements
Commonly recycled plastics include PET (bottles), HDPE (containers), and PVC (pipes). Recycled plastic significantly reduces greenhouse gas emissions and energy use during production.
For instance, recycling 1 kg of PET can lower global warming potential by 1.87 kg CO2 equivalent compared to virgin plastic.
Recycling technologies involve separation methods like gravity and electrostatic separation, as well as mechanical and chemical recycling processes. Mechanical recycling transforms plastic waste into granules for new products.
Advanced recycling techniques, such as chemical and pyrolysis, can break down even hard-to-recycle plastics into their chemical components, providing greater flexibility in repurposing them for new products.
Role of REGEN™ in Reducing Plastic Waste
Leading the way in the sustainable materials sector, REGEN™ specializes in biobased, renewable, and innovative plastics. Its bioplastics provide a sustainable substitute for conventional plastics made from chemicals sourced from fossil fuels.
As certified compostable, REGEN™ products safely break down and improve soil health. The company minimizes the effects of transportation by using locally sourced feedstocks and sustainable production methods that lower greenhouse gas emissions.
By promoting bioplastic production from agricultural waste, REGEN™ adds value to materials that would otherwise be discarded. Its cutting-edge materials are made for everything from food packaging to 3D printing.
Environmental Commitments by REGEN™
REGEN™’s innovative bioplastics and environmentally friendly business practices are part of its commitment to promoting sustainability and reducing its environmental footprint. The company uses renewable feedstocks to lessen reliance on fossil fuels and promote global sustainability goals.
It creates certified compostable products that safely break down, reducing hazardous residues and landfill waste. REGEN™ employs processes that lower greenhouse gas emissions and advocates for circular economy principles by designing products that facilitate recycling, composting, and reuse.
Their bioplastics offer superior performance while replacing traditional plastics. The company collaborates with a range of partners to promote eco-friendly practices. By consistently investing in R&D, REGEN™ hopes to lower costs and improve the performance of bioplastics, thereby securing its position as a leader in sustainable materials.
Key Takeaways
- The escalating threat of plastic pollution necessitates urgent and immediate action.
- Plastic is closely related to many aspects of modern life, but many behaviors can be modified to reduce unnecessary plastic waste.
- For implementation to succeed, industrial processes must evolve with consumption trends and regulatory frameworks.
- Recycling is a key element of managing plastic waste, and new technologies are increasing its effectiveness and environmental friendliness.
- Shifting to a circular economy framework manages plastic waste more effectively while prioritizing resource recovery and retention for longer product lifespans.
- REGEN™, a biobased bioplastic, is as practical as plastic but without harmful environmental impacts.
Frequently Asked Questions
Are There Any Global Agreements to Combat Plastic Pollution?
Global collaboration is essential for effectively mitigating plastic pollution. The United Nations Environment Assembly adopted a resolution (UNEA 5.2) to end plastic pollution in 2022.
The UNEA’s resolution paved the way for the development of the first internationally legally binding instrument on plastic pollution, including in the marine environment (ILBI).
The instrument includes provisions that support the creation and execution of National Action Plans (NAPs) aimed at preventing, reducing, and eliminating plastic pollution. NAPs are a standard tool for countries to address commitments within multilateral environmental agreements.
Can Banning Plastic Bags Significantly Reduce Plastic Pollution?
The demand for single-use plastic bags has reached 4.8 trillion annually, prompting many countries to ban them in favor of biodegradable, cloth, and paper bags.
While paper bags are recyclable and often made from eco-friendly materials, they generate 70% more air pollutants and 50 times more water pollution than plastic bags. Additionally, transporting paper bags requires seven times more trucks than plastic bags.
Are Biodegradable Plastics a Viable Solution?
Promoting bioplastics and compostable materials as viable solutions can reduce landfill pressure while helping protect the environment.
Sustainable plastics, such as REGEN™ PHA, have similar properties to traditional plastics while providing additional benefits due to their low carbon footprint. Selecting the best biodegradable material depends on the application, performance requirements, and environmental goals.





