The move toward PHA plastics is a result of people recognizing the polluting nature of traditional plastics and the countless problems those plastics cause for the planet.
PHA plastics are among the most talked-about bioplastics, prized for their versatility and myriad of applications. Benefits include being compostable, under the right conditions, and manufacturable using renewable materials.
It’s for these reasons that companies switch to PHAs to make food packaging, medical materials, and many other products.
This guide explores what PHA plastics are and highlights some of their many uses and advantages.
What Is PHA Plastic?
PHA plastics, or polyhydroxyalkanoates, are bioplastics. Bioplastics are alternatives to conventional plastics, synthesized from renewable biomass sources like plant sugars and lipids.
In the case of PHA plastics, bacterial fermentation enables production. This fermentation process requires a natural feedstock of some kind, like plant oils, but can also incorporate waste products, such as wood residue.
To start the process, the microorganisms receive the feedstock. They’re then subjected to specific conditions that encourage them to produce PHAs, which the microorganisms store as an energy reserve. The PHAs are then extracted or harvested from the bacteria and put through a purification process before they’re processed into usable plastic products.
Regen™ takes this process even further using a combination of BOSK-developed formulas. Blending PHAs with natural ingredients like wood fibers and biopolymers, Regen™ creates a material that’s as practical as plastic with none of the environmental downsides – discover Regen™ today.
Here are some of the unique properties that set PHA plastics apart from other bioplastics:
- Origin: PHA plastics are one of the few bioplastics manufacturers that can make using bacteria. PHBs (polyhydroxybutyrates) are another example. Most other bioplastics need different renewable resources like plant oils or cornstarch, which require more resources to produce.
- Biodegradability: PHAs are fully biodegradable, making them compostable plastics. They can decompose in marine environments and landfills within months. This differs from other bioplastics like PLAs (polylactic acids), which require controlled industrial conditions to break down. Natural biodegradation of these plastics can take decades.
- Mechanical Properties: PHA plastics offer high flexibility, exhibit good biocompatibility and offer tunable mechanical properties, too. They’re strong and durable, akin to conventional plastics in many ways, and deal with heat well. Most other bioplastics aren’t as tough.
- Barrier Properties: PHAs also have excellent barrier properties, meaning they do a good job of keeping out water vapor and gases. In this respect, they’re also superior to a lot of the other bioplastics out there, some of which are only good at keeping out specific gases like oxygen.
- Production Cost: Not all PHA’s unique aspects are positive. Compared to many other bioplastics, they have a high production cost due to the multi-stage production process and complex conditions involved in stimulating the bacteria to produce PHAs.
For a closer look at the leading producers in the PHA industry and how they are addressing production challenges, explore our detailed guide on the top PHA manufacturers shaping the future of sustainable plastics.
Applications of PHA Plastics
Since they provide good barrier properties and can be blended with other biopolymers, PHA plastics have a huge range of applications. They are used for cosmetic and food packaging.
Processing into films and fibers also allows PHAs to serve the 3D printing and medical sectors, with the latter using bioplastic for biodegradable surgical staples, wound dressings, and similar applications. PHA’s also show increasing potential in the agricultural sector.
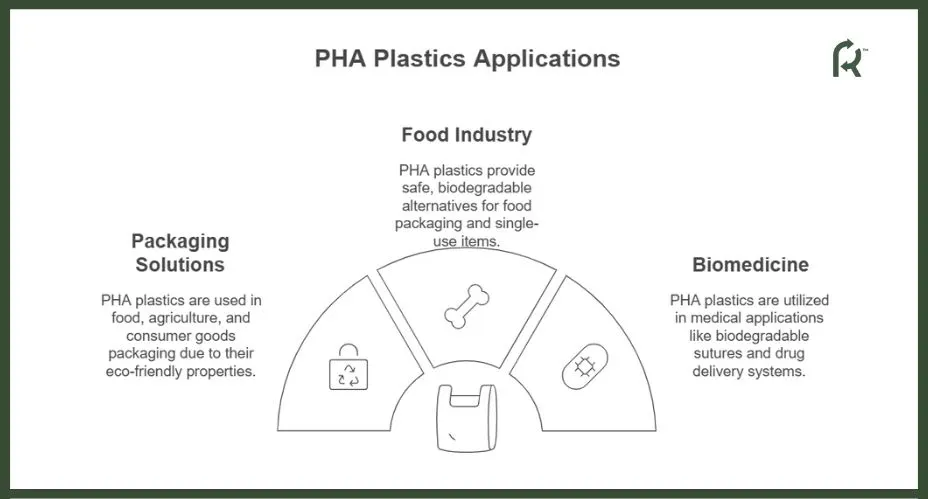
Packaging Solutions
Packaging is one of the primary uses for PHA plastics, thanks to their distinctive blend of characteristics. They’re used in:
- Food: PHA plastics are food-safe and thus suitable for use as containers, bags, and wrappings for snacks, yogurts, and fresh fruit and veggies, to name but a few examples.
- Agriculture: PHAs have proven popular in the agricultural sector, where they’re used as mulch films to guard against soil erosion or liners for seedling pots.
- Consumer Goods: You can use PHAs in consumer packaging, such as toothpaste tubes, toy boxes, and personal care product bottles.
To explore the various uses of PHA materials across industries, check out our comprehensive article on PHA material applications, highlighting how these bioplastics are transforming the packaging, healthcare, and agricultural sectors.
Since they exhibit thermoplastic properties like strong heat resistance, durability, and flexibility, PHAs work well for all the above kinds of packaging and more.
They can house, protect, and shield everything from everyday foods to fancy electronic devices, offering similar levels of sturdiness and reliability to conventional plastics but without the negative ecological impacts.
Food Industry
The food industry uses PHA plastics for food-safe packaging like yogurt containers and candy bags. In addition, they are suitable for single-use products like compostable knives, forks, and spoons. They’re also used to make drinking straws, providing an eco-friendly alternative to plastic straws.
Scientific experts agree that PHAs are ideal for applications throughout the food industry. In most cases, they’re completely food-safe and non-toxic, and they won’t pass on odors or flavors to the food items they protect, unlike some traditional plastics.
Moreover, the biodegradable nature of PHAs means that they can meet mankind’s extensive food packaging and disposable item needs without damaging the natural world.
Biomedicine
PHA plastics have medical applications, too. In fact, PHAs are a very exciting development for the evolving field of biomedicine, which focuses on applying biological research and innovations to the field of medical care. PHAs are used for sutures that dissolve in the body over time, tissue implants, and even drug delivery systems that can target specific cell groups or organs.
Factors that make PHA plastics so well-suited to biomedicine include:
- Biocompatibility: PHA plastics, in general, are gentle on the body and tolerated well. This means there’s less risk of any rejection or negative side effects when working with this material.
- Bioresorbability: The human body can break down PHA plastics naturally. PHA sutures can dissolve over time rather than having to be surgically removed, reducing the chance of infection.
Benefits of PHA Plastics for Eco-Conscious Brands
Petroleum-based plastics have played a significant role in climate change, pollution, and ecological devastation. As a result, modern and future-focused brands and organizations are beginning to eschew traditional plastics in favor of more ecologically sound alternatives. This strategy has significant advantages, especially for those who select PHA plastics to meet their plastic needs.
For starters, using PHA plastics or other bioplastics can bolster your brand’s green credentials. At a time when green consumerism is on the rise, you can’t understate the importance of going green.
People want to buy more sustainable products – 46% say they’re buying sustainable products to reduce their personal environmental impact. Transitioning to PHAs can broaden your brand’s appeal among your target audience.

Performance Advantages
One of the challenges of transitioning to bioplastics is that, unfortunately, most current bioplastics can’t match conventional plastics in metrics like strength and durability. But PHA plastics are different. With high innate levels of strength and toughness, they’re among the most effective of all bioplastics.
Variations in manufacturing and engineering processes create PHAs with different strength levels. Some are super strong and rigid, while others are more elasticated.
This diversity opens lots of doors to a wide range of applications. They can also have differing levels of flexibility, making them usable for everything from rigid packaging boxes to completely malleable wraps and liners.
PHA plastics also exhibit strong barrier properties, as touched on earlier. They can block out moisture and gases like oxygen, protecting sensitive contents (like foods) from degradation. This is effective for food packaging, where PHA plastic wraps and containers help to extend the shelf life of food items. Longer shelf life has the knock-on effect of reducing waste, helping the planet even more.
Traditional plastics are also able to extend the shelf life of foods and also come in many different forms with different levels of strength and flexibility.
However, their production often causes harm to the natural world. You reduce this harm when using PHAs, enabling us to have the best of both worlds – all the strength and protection of plastic but without the downsides.
Environmental Benefits
When it comes to reducing the impact on the environment, few bioplastics can match PHAs:
- Biodegradable: They decompose quickly, efficiently, and safely anywhere in the natural world. You can toss PHA plastic products into water or landfills, and they’ll break down through microbial activity in a matter of months. RegenTM, for instance, breaks down within 180 days without requiring industrial composting processes.
- Compostable: They can be processed in industrial composting facilities, with appropriate heat and humidity controls to optimize the process. They break down into completely safe and natural elements like carbon dioxide and can even replenish the soil as it decomposes.
PHAs have a notably smaller carbon footprint compared to conventional plastics. Lifecycle assessments prove this, showing that the processes and resources involved in making, using, and disposing of PHA plastics have a smaller carbon footprint than that of petroleum-based plastics. PHAs contribute to up to 75% of positive ecosystem quality endpoint impacts when compared to these traditional plastics.
If you’re deciding between these two leading bioplastics, read our side-by-side comparison of PLA vs PHA to understand their environmental impacts and performance in various applications.
Regen™ and PHA: Advanced Sustainable Solutions
PHA plastics rank among the very best bioplastics available right now. But they’re not perfect. There are challenges in the large-scale production of PHAs as they require specific creation processes and conditions.
It’s up to corporate innovators to keep improving PHAs, to push the boundaries of what they can do and how they’re made, while promoting wider acceptance and application of these sustainable materials.
That’s where Regen™ comes in. Regen™ is an innovative Canadian company focused on exciting, efficient, and eco-friendly bioplastics. This Canadian base reduces reliance on imported materials, minimizing the environmental impact so often seen in PHA production.
Crafted from nothing but renewable resources and building on the foundations established by PHAs, Regen™ bioplastic is bio-based, compostable, non-toxic, and high-performance, leading the way in bioplastic development and solutions.
Innovations by Regen™
Regen™’s innovative bioplastic takes PHA further with the following benefits:
- Flexible: Regen™’s bioplastic can exhibit variable, modular, and mechanical properties to suit an array of specific and niche applications.
- Local: Regen™’s bioplastics are designed, developed, and made in Canada. This reduces its carbon footprint by eliminating long-distance transport costs.
- Compostable: Regen™ ‘s plastic meets strict ASTM D6400 compostability standards. It breaks down in less than six months at industrial facilities.
- PHA+: PHA plastics form the basis of Regen™. But we also add ingredients like natural biopolymers and additives to enhance its properties.
Thanks to Regen™’s innovation, an even brighter future lies ahead for PHA-based bioplastics. They’ve already contributed and accomplished so much, but Regen™ is proof that PHAs can be even more – more sustainable, more flexible, and more useful.
In the years ahead, innovative plastics like these could well replace the conventional petroleum plastics that have polluted the world for decades.
Commitment to Sustainability
Sustainability is Regen™’s driving force. It’s why we’re so committed to pushing the boundaries of bioplastics and making them the best they can be.
It’s also why our innovative PHA-based bioplastic is not only biodegradable but compostable, locally-made, bio-based (produced from renewable natural materials), and non-toxic.
- Regen™ bioplastic has TUV Austria certification, which confirms it is a biobased plastic made using renewable raw materials, not from fossil fuels or their derivatives.
- Regen™ meets ASTM D6400 and ISO 17088 standards of compostability.
Discover Regen™ today – our PHA products include cosmetic packaging and 3D filaments.
Key Takeaways
- PHA plastics are one of the most popular and useful examples of bioplastics.
- These plastics are naturally produced by microorganisms like bacteria.
- They’re used in many industries, like food, healthcare and agriculture.
- Some of their benefits include strength, flexibility, and compatibility with other substances.
- They’re 100% biodegradable, breaking down naturally via microbial action.
- PHAs aren’t perfect, and innovators like Regen™ aim to make them even better.
Frequently Asked Questions
Is PHA Plastic Environmentally Friendly?
Yes, especially compared to conventional petroleum-based plastics. It’s biodegradable in a wide range of settings (like soil and water) and has a smaller carbon footprint than traditional plastics. Plus, it’s made with renewable natural resources. However, it still requires energy to produce, meaning the plastic has an environmental impact.
Is PHA Plastic Recyclable?
Yes, but only through specific methods. Research is ongoing to find the best mechanical and chemical ways to reuse PHA, which may include melting it down and reshaping it or using chemicals to break it down. As a result of this research, we may discover even more efficient and less energy-intensive ways to break down and recycle PHA plastics.
Can PHA Plastics Be Used in All Types of Packaging?
PHA plastics are versatile and usable for a broad range of packaging types, including food wraps and bags, consumer goods containers, and films and linings. However, their heat sensitivity restricts their application in hot settings, such as ovens and industrial settings that exceed the 104 to 356-degree Fahrenheit limit of the PHA. This limit varies depending on the PHA’s manufacturing process.





